What does a Furnace Filter do?
The furnace filter keeps dust out of the furnace’s internal components & also aids in the cleaning of larger particles from your home’s air. It is important you have the correct filter for the furnace. The wrong size and/or rating may damage or reduce the performance of your furnace.
Where is your filter?
The filter is located somewhere between the ductwork and the furnace. There should be an easy access point, often called a filter rack, that is designed to easily change out your filter.
Filters: When To Change It
- If you are unsure the of the last filter change, and can see it is dirty, change it ASAP.
- Every six months or at the start of the heating & cooling season.
- If you have pets check the filter every 3 months to ensure it is not too clogged.
- Snap a picture of the rating plate or the old filter to save the record of what size you need.
Which Size Filter Should I Use?
- What are the filter’s dimensions?
- What MERV rating does the filter have?
The best place to check is in the user’s manual that came with your furnace OR you can open the door of your furnace and look for what is called the rating plate.
-
Open the blower door panel of your furnace (usually the bottom front panel).
-
Inside, there’s often a sticker or label that lists the correct filter size and recommended MERV range.
Where Do I Buy Them?
- Get them as a part of a annual maintenance package from the company who installed the furnace.
- Purchase them from a big box store (if in stock)
- Call a local HVAC company to check availability
Are there reusable Furnace Filters options?
Not really. Yes, there are some very low rated options, but since they offer poor protection, the industry standard remains the thicker disposable ones. While it is not great for the environment, it is no different to the cabin filter in your car, and sometimes it works better as a disposable object.
Furnace Filter
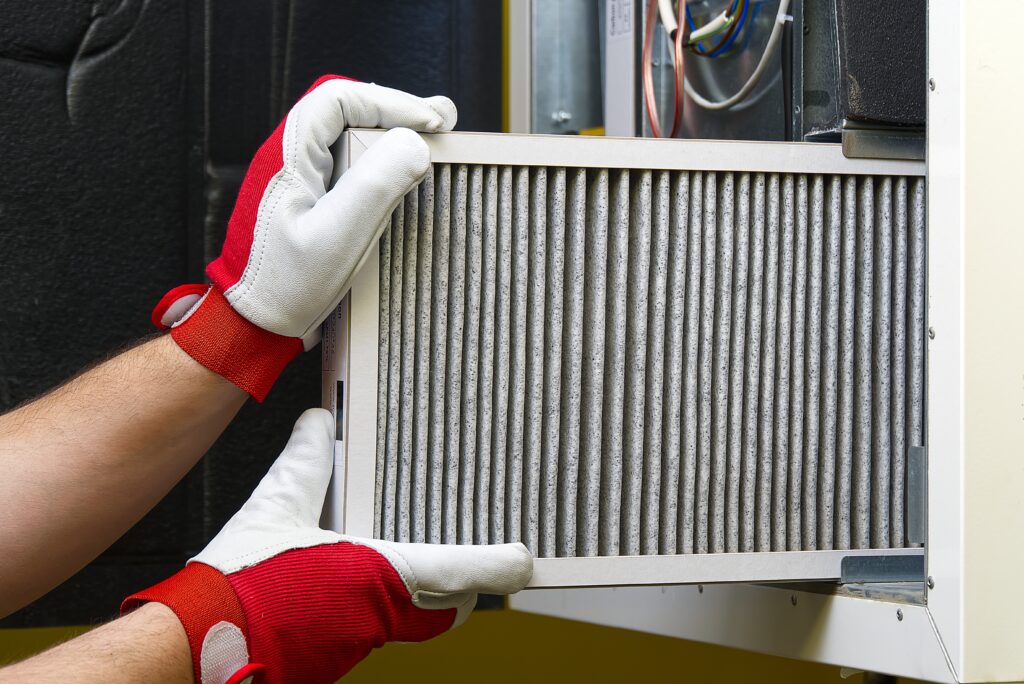

The furnace filter is located next to the duct work where is connects to the furnace
Filter Location

Clean Filter Vs Dirty Filter

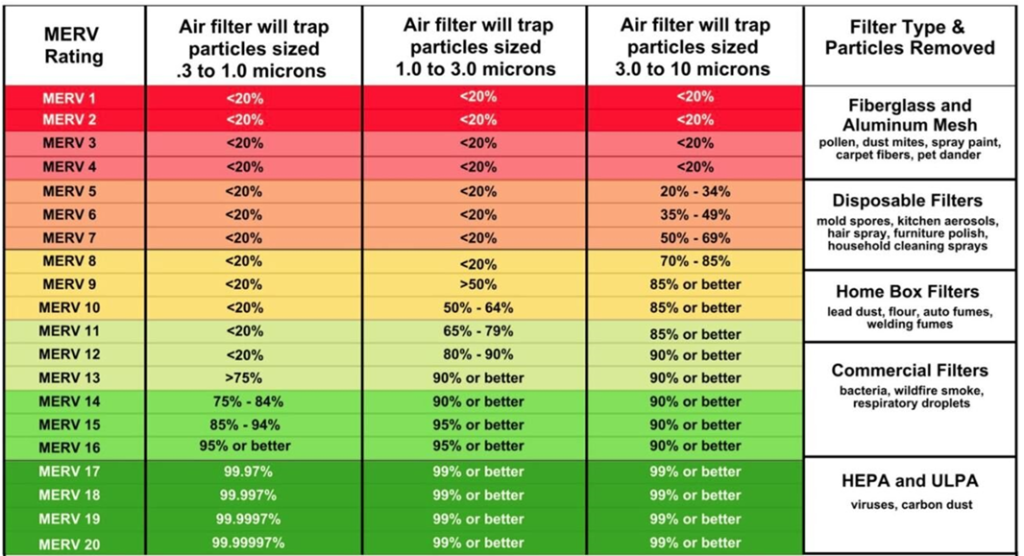
MERV Filtration

Filter Ratings (MERV)
Every furnace filter has a rating, but the furnace is designed to work with range of filter ratings. If the rating is too low it offers minimal benefits, but if it is rated too high, it can impede air flow leading to equipment performance issues.
Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value.
It’s a rating system that measures how effectively an air filter traps particles of different sizes. The MERV scale runs from 1 to 16 (or up to 20 in some high-efficiency systems):
-
-
Low MERV (1–4): basic dust and lint filtering.
-
Medium MERV (5–8): captures mold spores, pet dander, and pollen.
-
High MERV (9–12): traps finer particles like lead dust or auto emissions.
-
Very High MERV (13–16): near-HEPA level — removes bacteria, smoke, and fine allergens.
-
MERV Ratings in Detail
The below chart breaks down the parameters used to filter the air of harmful particulates.
Some things are smaller than other things, for example pollen is comparatively larger to other particulates. While, viruses, the most harmful, are incredibly small.
That means most filters can trap pollen while very few filters can actually capture air borne viruses.
High filtration always comes at the cost of air flow, the thicker the filter, the larger impact it has on how fast air can move through the filter.
Typical Filters & Labels


Gas Furnace Diagram
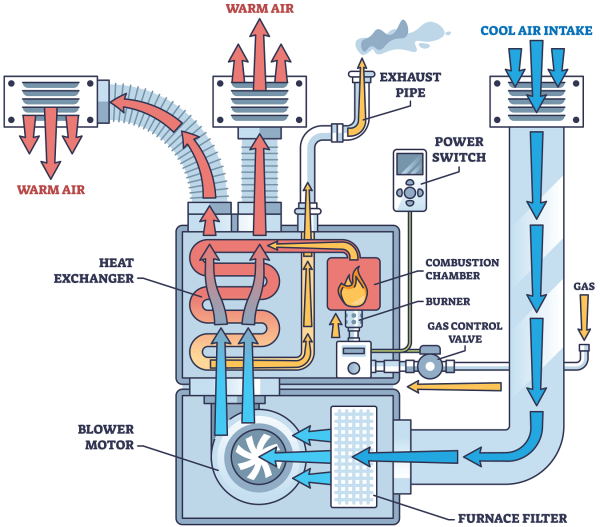
Burner: Ignites gas to create heat.
Draft Inducer: Pulls air into the burner and pushes exhaust outside.
Heat Exchanger: Transfers heat from the flame to the air.
Igniter/Pilot Light: located in the burner & starts the burner flame.
Thermostat: Controls when the furnace turns on or off.
Blower Fan: Circulates warm air through the home.
Exhaust: Releases exhaust gases safely outdoors.
Furnace Filter: Cleans air before it enters the furnace.
Combustion Chamber: Where the gas burns to produce heat.
Warm Air Vent: Delivers heated air into the rooms.
Cold Air Vent: Brings cool air back to the furnace.
Power Switch: Safety switch for the furnace’s electrical system: on or off.
Gas Control Valve: Regulates gas flow to the burners.
- Gas: the propane or natural gas hook up











